Page 72 - eBook_Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Manufacturing V1
P. 72
Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Manufacturing –
Volume 1
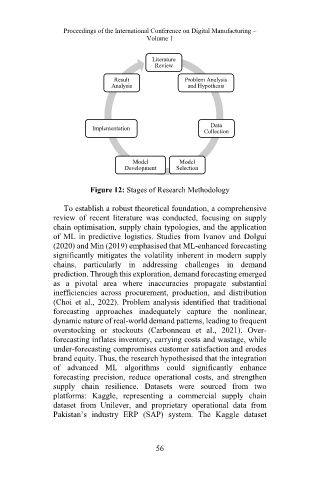
Literature
Review
Result Problem Analysis
Analysis and Hypothesis
Data
Implementation Collection
Model Model
Development Selection
Figure 12: Stages of Research Methodology
To establish a robust theoretical foundation, a comprehensive
review of recent literature was conducted, focusing on supply
chain optimisation, supply chain typologies, and the application
of ML in predictive logistics. Studies from Ivanov and Dolgui
(2020) and Min (2019) emphasised that ML-enhanced forecasting
significantly mitigates the volatility inherent in modern supply
chains, particularly in addressing challenges in demand
prediction. Through this exploration, demand forecasting emerged
as a pivotal area where inaccuracies propagate substantial
inefficiencies across procurement, production, and distribution
(Choi et al., 2022). Problem analysis identified that traditional
forecasting approaches inadequately capture the nonlinear,
dynamic nature of real-world demand patterns, leading to frequent
overstocking or stockouts (Carbonneau et al., 2021). Over-
forecasting inflates inventory, carrying costs and wastage, while
under-forecasting compromises customer satisfaction and erodes
brand equity. Thus, the research hypothesised that the integration
of advanced ML algorithms could significantly enhance
forecasting precision, reduce operational costs, and strengthen
supply chain resilience. Datasets were sourced from two
platforms: Kaggle, representing a commercial supply chain
dataset from Unilever, and proprietary operational data from
Pakistan’s industry ERP (SAP) system. The Kaggle dataset
56